Quercetin: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Quercetin is a plant-derived antioxidant found in many fruits and vegetables, studied for its anti-inflammatory and longevity-enhancing potential.
Read More
Niacin: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Niacin, or vitamin B3, plays a vital role in energy metabolism and may influence aging pathways through NAD+ modulation.
Read More
Apigenin: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Found in chamomile, apigenin is a natural flavonoid with reported anti-inflammatory and anti-anxiety effects, and potential cellular benefits.
Read More
Magnesium: Benefits and Side Effects
Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and has been explored for its role in aging and chronic disease prevention.
Read More
Rapamycin: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Rapamycin is one of the most studied compounds in longevity science, known to extend lifespan in multiple species by inhibiting mTOR.
Read More
Creatine: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Best known for athletic performance, creatine is also being explored for neuroprotection and cognitive aging support.
Read More
Spermidine: Benefits, Research, and Side Effects
Spermidine is a polyamine that promotes autophagy and may mimic some of the effects of caloric restriction to support healthspan.
Read More
Yamanaka Factors: Opportunities for Rejuvenation
The Yamanaka factors (OSKM) can reprogram cells to a more youthful state, holding promise for reversing age-related cellular changes.
Read More
Vitamin K2: Uses and Possible Side-Effects
Vitamin K2 is essential for bone and cardiovascular health, and emerging research is exploring its role in longevity and immune function.
Read More
Ashwagandha: Benefits, Uses, and Side-Effects
Ashwagandha is an adaptogenic herb known for its ability to reduce stress and anxiety, support cognitive function, and improve overall vitality.
Read More
Centrophenoxine: Research, Benefits, and Side-Effects
Centrophenoxine is a cholinergic compound studied for memory enhancement and neuroprotection, potentially useful in age-related cognitive decline.
Read More
Improving Sleep Quality for Better Health
Better sleep improves cognitive function, immune resilience, and mental health. This article explores evidence-based techniques to improve sleep hygiene.
Read More
Biotin: Side Effects and Benefits You Should Know About
Biotin supports healthy hair, nails, and skin, and plays a crucial role in metabolic processes, although supplementation can sometimes skew lab tests.
Read More
L-Carnitine: Benefits, Uses, and Side Effects
L-Carnitine helps transport fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production and has been explored for cardiovascular and cognitive health benefits.
Read More
Apple Cider Vinegar: Benefits, Myths, and Side Effects
Apple cider vinegar is popular for purported digestive and weight benefits, though evidence is mixed and high doses may cause side effects like enamel erosion.
Read More
Intermittent Fasting and Time-Restricted Feeding
Intermittent fasting may reduce inflammation, improve metabolic health, and influence longevity, though long-term human data is still emerging.
Read More
How Metabolic Syndrome Makes Aging Worse
Metabolic syndrome accelerates aging by increasing inflammation and oxidative stress, raising the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Read More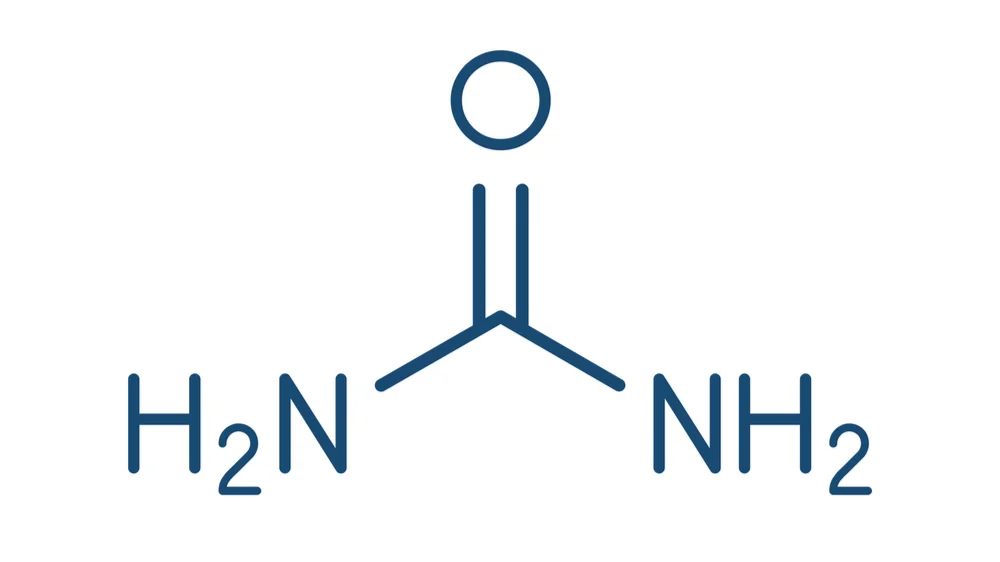
Urea Is a Blood Biomarker of Aging
Though traditionally used to monitor kidney health, elevated urea levels are now being investigated as indicators of systemic aging processes.
Read More
Red Blood Cells as Biomarkers of Aging
Alterations in red blood cell distribution width and deformability are emerging as potential indicators of biological aging and disease risk.
Read More
The Relationship Between ApoE and Alzheimer’s
The APOE ε4 allele is the strongest known genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, shaping research into personalized prevention strategies.
Read More
Blood Glucose Is a Biomarker of Aging
High fasting blood glucose is linked to insulin resistance and shorter lifespan, making it a key target for interventions in aging biology.
Read More
What Alkaline Phosphatase Is and Does
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme tied to bone and liver health. Elevated levels are associated with aging and chronic disease risk.
Read More
Albumin as a Blood Biomarker of Aging
Low serum albumin levels are linked to frailty, inflammation, and mortality in older adults, making it a valuable biomarker in longevity science.
Read More
Hyaluronic Acid: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Hyaluronic acid is essential for skin hydration and joint health, with research also exploring its role in wound healing and inflammation reduction.
Read More
Butyrate: Health Benefits and Side Effects
Butyrate is a gut-derived short-chain fatty acid linked to improved gut health, reduced inflammation, and possible metabolic benefits in aging.
Read More
Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Alpha-lipoic acid is a mitochondrial antioxidant that may enhance glucose metabolism, reduce oxidative stress, and support cognitive and liver health.
Read More
Resveratrol: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Resveratrol is a polyphenol associated with heart health and lifespan extension in animals, partly due to its activation of sirtuin pathways.
Read More
Metformin: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Metformin is a diabetes medication that’s being studied for its potential to delay aging and reduce cancer and cardiovascular risk in non-diabetics.
Read More
Chondroitin Sulfate: Benefits, Side Effects, and Research
Commonly used for joint health, chondroitin sulfate may reduce inflammation and cartilage degradation, with emerging interest in its anti-aging properties.
Read More
Low-Dose Naltrexone: Benefits and Side Effects
Low-dose naltrexone is being researched for its immune-modulating and anti-inflammatory effects, showing promise for autoimmune and chronic pain conditions.
Read More
What Is Glutathione? A Summary of Glutathione
Glutathione is the body’s master antioxidant, critical for detoxification, immune health, and cellular repair, with levels declining with age and illness.
Read More
How Sleep Apnea Accelerates Biological Aging
Alarmingly common yet routinely ignored, severe untreated obstructive sleep apnea can steal 7 to 8 years of life, second only to cigarette smoking.
Read More