Project Title: RESET – Resilience & Epigenetic Signatures of Early‐Life Trauma
Overall Objective: Quantify how cumulative childhood adversity accelerates biological ageing—and test whether trauma‑focused cognitive‑behavioural therapy (TF‑CBT) and lifestyle optimisation can decelerate that trajectory—using multi‑clock epigenetic profiling combined with psychological, inflammatory and lifestyle data in a racially diverse cohort of youth and young adults.
1. Specific Aims (24‑month R21‑scale pilot)
| # | Aim | Primary Metric |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cross‑sectional link between Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE) score and multi‑clock age acceleration at baseline. | PedBE (8–17 y), GrimAge & DunedinPACE (18–35 y) residuals |
| 2 | Mechanistic mediators – quantify the contribution of systemic inflammation (CRP, IL‑6) and HPA‑axis activity (diurnal & hair cortisol) to the ACE→clock association. | % mediation in path models |
| 3 | Intervention deceleration – test whether 16 weeks of TF‑CBT + home‑based activity/sleep optimisation slows DunedinPACE vs wait‑list control over 12 months. | ΔDunedinPACE/yr |
2. Study Design
- Population: 400 participants (n = 250 aged 8–17; n = 150 aged 18–35), oversampling high‑ACE strata via community mental‑health partners.
- Sampling: Buccal swab (PedBE) for <18 y; EDTA blood for ≥18 y.
- Assessments: ACEs questionnaire, PTSD/depression scales, CD‑RISC resilience, actigraphy (7 d sleep & MVPA), salivary diurnal cortisol (4‑point), hair cortisol, plasma CRP & IL‑6.
- Intervention Arm: 16‑week TF‑CBT (telehealth) + personalised sleep/PA coaching; 1:1 randomisation within high‑ACE strata.
- Follow‑up: Baseline, 12 m, 24 m biospecimen & survey waves.
3. Power and Sample Size Simulation
3.1 Static Results
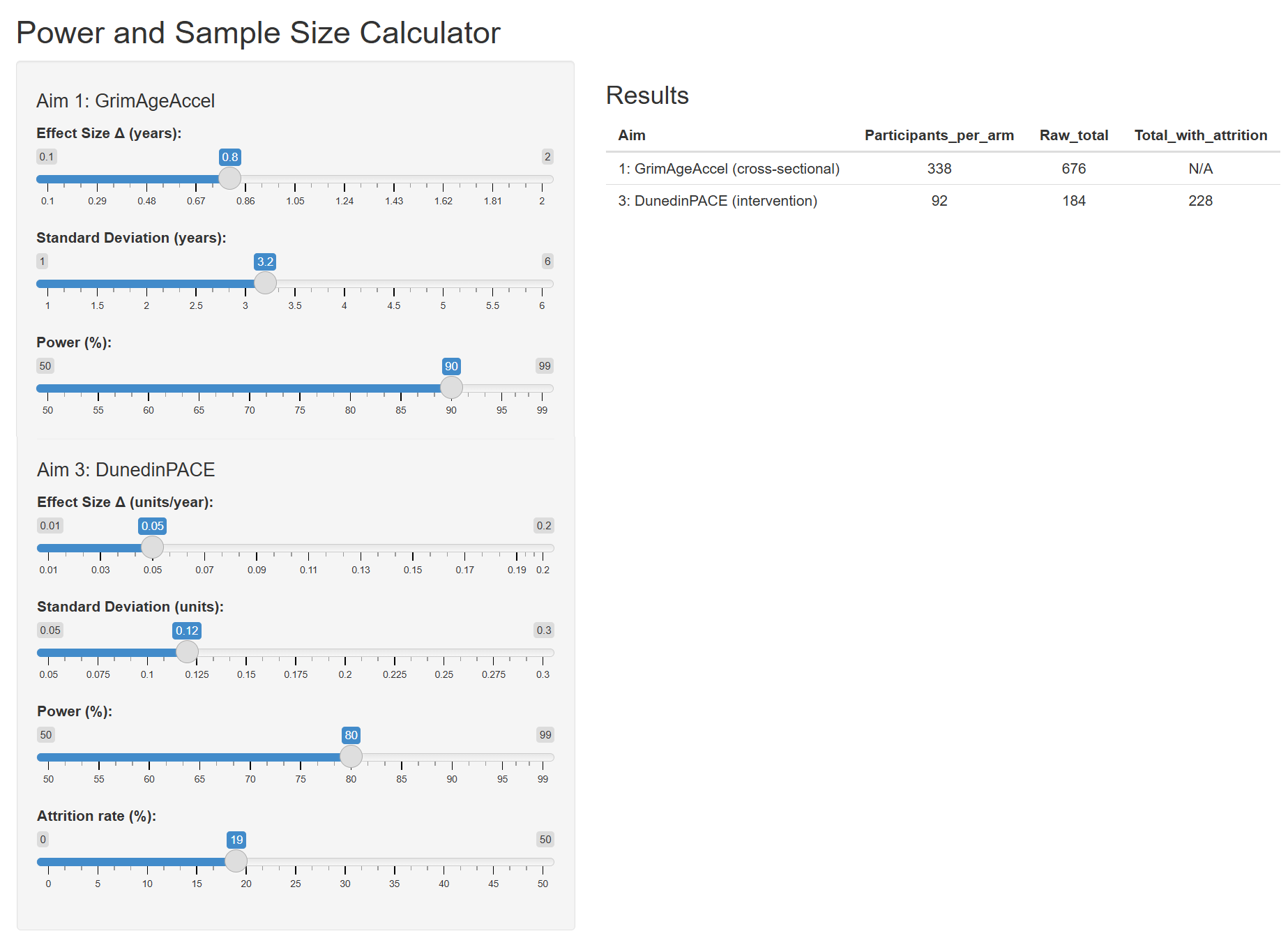
| Aim | N per group/arm | Raw total | Total with 15 % attrition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Cross‑sectional) | 338 | 676 | – |
| 3 (Intervention) | 92 | 184 | 216 |
3.2 Narrative Summary
Power calculations were performed in R (pwr package) using two‑sample t‑tests at a two‑sided α = 0.05. For Aim 1 (≥4 vs 0 ACEs), detecting a 0.8‑year GrimAgeAccel difference (SD = 3.2 y) with 90 % power requires 338 participants per arm (676 total). For Aim 3, detecting a 0.05‑unit/year change in DunedinPACE (SD = 0.12 units) with 80 % power requires 92 participants per arm (184 total), inflated to 216 to allow for 15 % attrition.
3.3 Interactive Power and Size Calculator
Use this calculator to determine the appropriate sample size based on the expected difference, desired confidence level, and data variation.
4. Budget Outline (USD, 2‑year project)
5. Timetable & Milestones
| Quarter | Milestone |
| Q1–Q2 | IRB approval & FWA finalised; REDCap database live; community advisory board convened. |
| Q2–Q3 | First 100 participants enrolled; lab contracts executed; actigraphy & biospecimen workflows debugged. |
| Q3–Q4 | Randomise first 40 high‑ACE participants to TF‑CBT; interim QC report on methylation data. |
| Year 2 Q1 | Enrollment complete (n = 400); 50 % have 12‑month visit. |
| Year 2 Q3 | Data freeze for R01 power simulation; draft Specific Aims. |
| Year 2 Q4 | Analyses complete; manuscript submitted; NIH R01 application filed. |
6. Potential Funding Mechanisms
- NIH NIA / NICHD R21 – PAR‑25‑218 “Novel research infrastructure to advance the science of aging.”
- CDC Injury Center FOA RFA‑CE‑25‑025 – “ACEs research translation.”
- California ACEs Aware mini‑grants – Policy translation ($200–500 k).
- Corporate co‑sponsorship: TruDiagnostic / Zymo Research (in‑kind assay discounts).
7. Contact
PI: , Stephen C. Rose PhD – Bioengineering. Chris@Geronimo.life
Co‑I (Psych): Adam O’Brian, PhD – Psychology.
Draft v1.0 – June 2025
